Defibrillators
Defibrillators
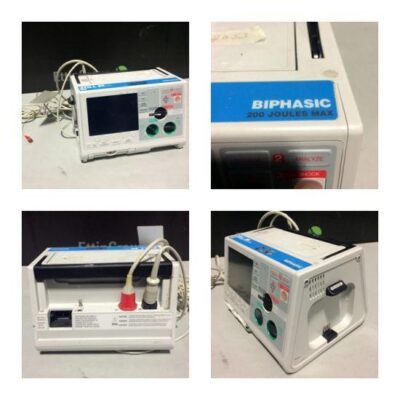
Defibrillators Defibrillation is a process in which an electronic device gives an electric shock to the heart. This helps reestablish normal contraction rhythms in a heart having dangerous arrhythmia or in cardiac arrest. In recent years small portable defibrillators have become available. These are called automated external defibrillators or AEDs.
Defibrillation is a treatment for life-threatening cardiac dysrhythmias, specifically ventricular fibrillation (VF) and non-perfusing ventricular tachycardia (VT). A defibrillator delivers a dose of electric current (often called a countershock) to the heart. Defibrillation is a treatment for life-threatening cardiac dysrhythmias, specifically ventricular fibrillation (VF) and non-perfusing ventricular tachycardia (VT). A defibrillator delivers a dose of electric current (often called a countershock) to the heart. The electrical shock does not have to be timed with the heart’s intrinsic cardiac cycle. This depolarizes a large amount of the heart muscle, ending the dysrhythmia. Subsequently, the body’s natural pacemaker in the sinoatrial node of the heart is able to re-establish normal sinus rhythm.
In contrast to defibrillation, synchronized electrical cardioversion is an electrical shock delivered in synchrony to the cardiac cycle. Although the person may still be critically ill, cardioversion normally aims to end poorly perfusing cardiac dysrhythmias, such as supraventricular tachycardia.Defibrillators can be external, transvenous, or implanted (implantable cardioverter-defibrillator), depending on the type of device used or needed. Some external units, known as automated external defibrillators (AEDs), automate the diagnosis of treatable rhythms, meaning that lay responders or bystanders are able to use them successfully with little or no training
Showing all 2 results


Recent Comments